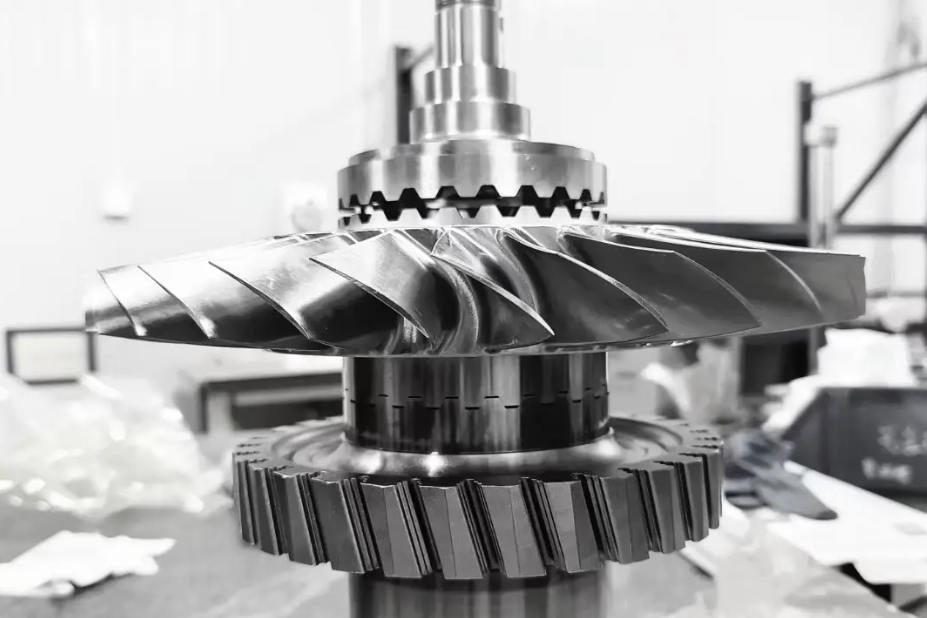
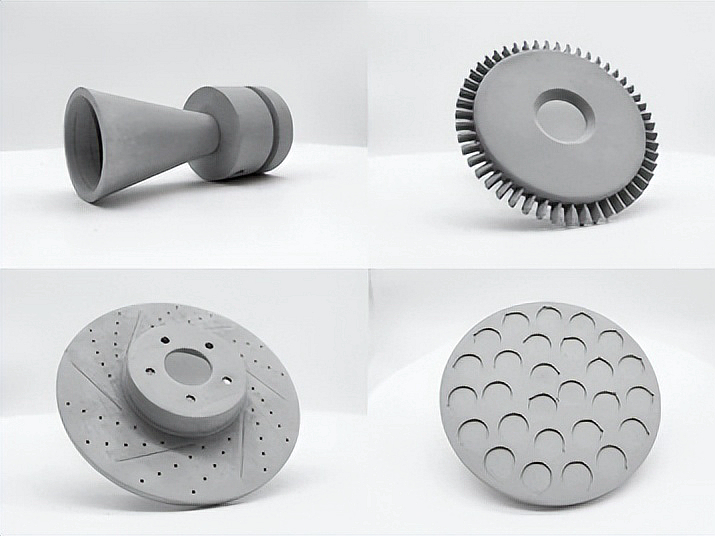
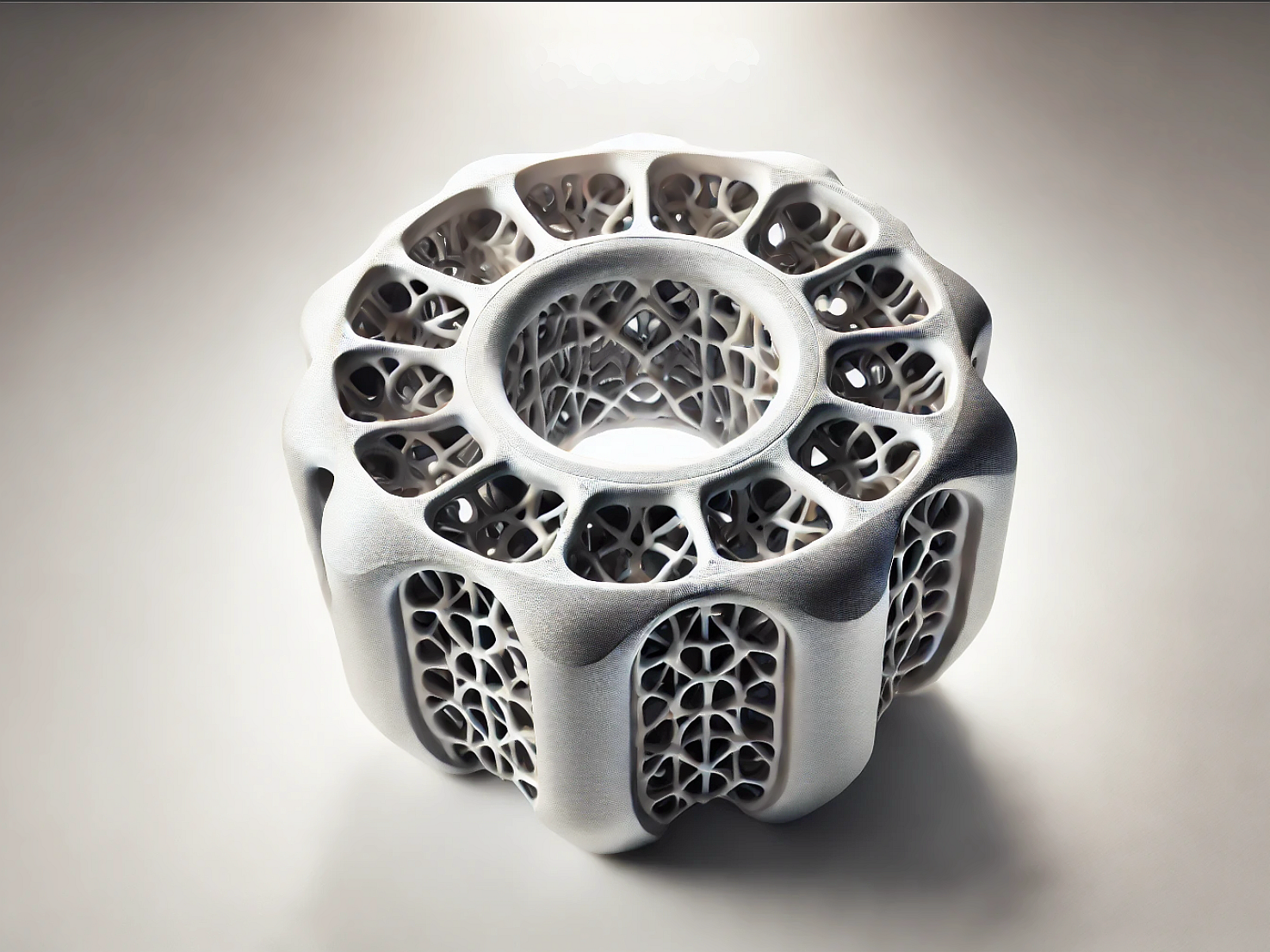
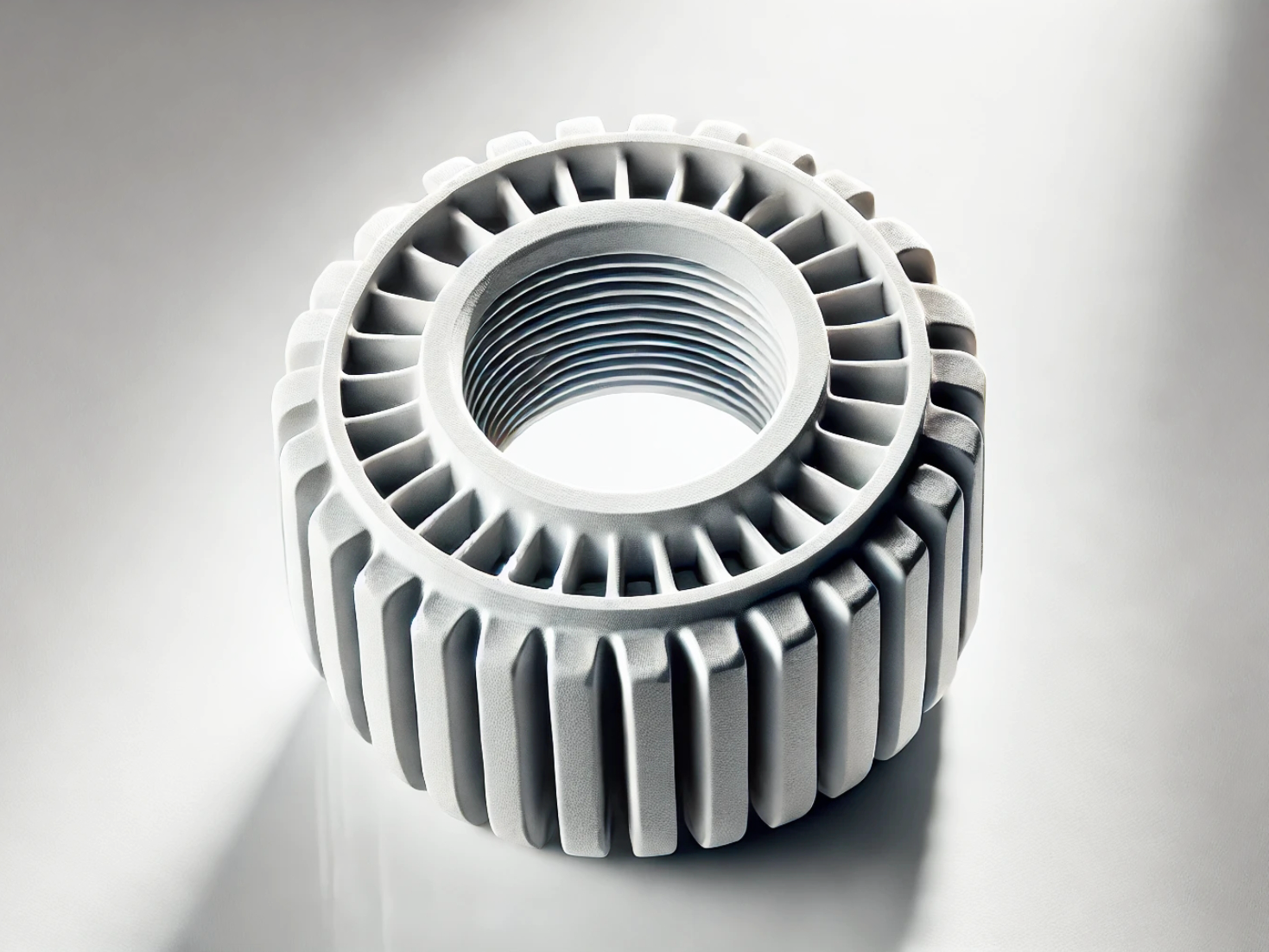
Advanced Ceramic Parts 3D Printing Service
Experience precision and innovation with our titanium parts 3D printing service. Utilizing Powder Bed Fusion, Binder Jetting, Sheet Lamination, and Directed Energy Deposition, we deliver high-quality, customized titanium components for diverse applications.

Send us your designs and specifications for a free quotation
All uploaded files are secure and confidential
Ceramic 3D Printing Technologies
Titanium 3D printing technologies include Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS). These methods excel in producing lightweight, high-strength parts with excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for aerospace, medical, and industrial applications.
Ceramic 3D Printing Materials
Post Process for 3D Printed Ceramic Parts
Post-processing for 3D printed ceramic parts enhances mechanical properties, surface finish, and functionality. Techniques like CNC machining, heat treatment, HIP, and coatings improve strength, durability, and thermal resistance, ensuring optimal performance for industrial, aerospace, and medical applications.
Applications of Ceramic 3D Printed Parts
Ceramic 3D printed parts are known for their exceptional thermal resistance, chemical stability, and electrical insulation properties. These characteristics make them highly suitable for applications in high-temperature environments, electronics, and medical devices. Key applications include heat exchangers, insulating components, and bespoke implants.
Ceramic 3D Printed Parts Case Study
Ceramic 3D Printed Parts Case Study explores the impact of advanced ceramic 3D printing in aerospace, medical, and industrial applications. From zirconia dental implants to silicon carbide aerospace components and alumina mechanical seals, this study highlights how high-performance ceramics provide wear resistance, heat tolerance, and precision in critical engineering and technological solutions.
Let's Start A New Project Today
Ceramic 3D Printed Parts Design Considerations
When designing ceramic 3D printed parts, it's essential to consider factors such as wall thickness, tolerance, and thermal management to ensure part integrity and performance. Ceramic materials require specific considerations due to their brittleness and thermal properties. Key design aspects include ensuring proper sintering and minimizing stress concentrations to prevent cracking.
Ceramic 3D Printed Parts Manufacturing Considerations
Manufacturing considerations for ceramic 3D printed parts focus on the material's brittleness and the complexity of sintering processes. Key aspects include managing sintering shrinkage, optimizing part strength through careful design and post-processing, and achieving precise dimensional accuracy.